Are you ready to unlock the hidden powers of your PC? Welcome, tech enthusiasts, to a thrilling journey into the captivating world of computer hardware! In this comprehensive guide, we will embark on an exhilarating adventure to demystify the heart and soul of any computer system: the motherboard.
Whether you are new to the world of PCs or an experienced user, this chapter will help you understand the vital role that the motherboard plays in your computer’s performance. You can take your PC to the next level by unlocking its full potential.
The Heartbeat of Your PC: Discovering the Motherboard’s Hidden Powers
Imagine a motherboard as the central nervous system of your computer. The primary circuit board connects all other hardware components, allowing them to communicate and work together seamlessly. Without a motherboard, your PC would be a collection of separate parts.
Let’s dive deeper into the various components that make up a motherboard and their functions.
CPU Socket
The CPU socket is like a docking station for your processor. It provides the necessary electrical connections and physical support for the CPU to operate efficiently. Specific processor families, like Intel’s LGA (Land Grid Array) and AMD’s AM4, have designed different sockets.
For example, if you have an Intel Core i7 processor, you need a motherboard with an LGA 1200 socket to ensure compatibility. Similarly, if you have an AMD Ryzen 5 processor, you would require a motherboard with an AM4 socket.
RAM Slots
Random Access Memory (RAM) slots are where you install memory modules, allowing your computer to store and quickly access data. Motherboards typically have multiple RAM slots, enabling you to increase your system’s memory capacity.
For instance, if you want to upgrade your system’s memory from 8GB to 16GB, you can add an 8GB RAM module to an empty RAM slot on your motherboard.
Expansion Slots
Expanding the slots makes connecting additional hardware components like graphics cards, sound cards, and network cards feasible. Two of the most widely used slot types are PCIe (Peripheral Component Interconnect Express) and PCI (Peripheral Component Interconnect) slots.
Suppose you’re a gaming enthusiast and want to enhance your graphics performance. You can install a dedicated graphics card into an available PCIe slot on your motherboard. Using this will significantly improve your enjoyment of playing games.
Storage Interfaces
Motherboards offer various storage interfaces to connect your hard drives or solid-state drives (SSDs). SATA (Serial ATA) and M.2 are popular interfaces that determine the speed and compatibility of your storage devices.
For example, if you have a high-performance SSD, you can use the faster data transfer speeds offered by an M.2 slot on your motherboard.
Power Connectors
Power connectors ensure that your motherboard and other components receive the necessary electrical supply. The primary power connector is typically a 24-pin ATX connector, while the CPU socket requires an additional power connector.
For instance, when building a new PC, you must connect the 24-pin ATX power connector from your power supply unit (PSU) to the corresponding socket on your motherboard. Additionally, you’ll need to click the CPU power connector (usually 4 or 8 pins) from the PSU to the CPU socket.
Size Matters: Choosing the Perfect Motherboard for Your Epic Build2.1 Form Factors: What Fits Your Needs?
Motherboards come in different form factors, each offering distinct advantages and limitations. Let’s explore some common form factors.
ATX (Advanced Technology eXtended)
ATX is the most popular form factor, offering a balance of expandability and compatibility. It features multiple expansion slots and sufficient space for additional components.
Suppose you’re building a gaming rig with multiple graphics cards, additional storage devices, and expansion cards. In that case, an ATX motherboard will provide ample room for all your requirements.

Micro-ATX (mATX)
Micro-ATX motherboards are smaller than ATX but still offer decent expandability. They are ideal for compact systems with limited space.
If you’re building a budget-friendly PC for everyday tasks or a small form factor (SFF) PC for media streaming, a micro-ATX motherboard will suit your needs while saving space.

Mini-ITX
If you’re looking to build a compact, space-efficient system, Mini-ITX is the way to go. While it sacrifices expansion slots, it offers impressive functionality in a tiny package.
Imagine building a home theater PC (HTPC) or a gaming console-sized PC. A Mini-ITX motherboard will provide the necessary features and performance while occupying minimal space.

Choosing a motherboard that supports your desired CPU socket type is crucial to avoid compatibility issues. Different generations and brands of processors require specific sockets, so ensure compatibility before making a purchase.
For example, if you plan to use an Intel Core i9-12900K processor, you’ll need a motherboard with an LGA 1700 socket. Always check the CPU compatibility list provided by the motherboard manufacturer to ensure a proper match.
Unleashing the Beast Within Exploring Chipsets and Unleashing Your PC’s Full Potential
Chipsets are integral to motherboards, facilitating communication between the CPU, memory, expansion slots, and other peripherals. Let’s delve into the two main types of chipsets.
King of the North: Northbridge
The Northbridge handles high-speed communication between the CPU, RAM, and graphics card. It determines your system’s overall performance. The CPU or the system-on-a-chip (SoC) integrates Northbridge’s functions in modern motherboards. For example, AMD’s Ryzen processors include an integrated memory controller and PCIe lanes, reducing the need for a traditional Northbridge chipset.
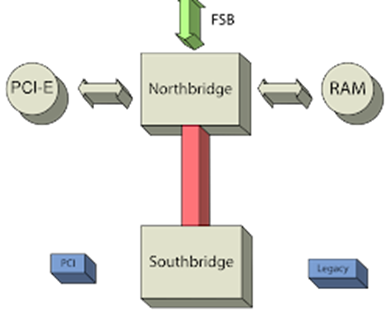
Queen of the South: Southbridge
The Southbridge manages lower-speed communication between the CPU, storage devices, and I/O interfaces. It handles tasks like USB connectivity, SATA ports, and audio.
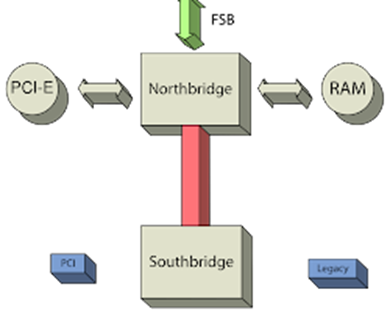
For instance, when you connect a USB flash drive to your PC, the Southbridge facilitates the data transfer between the USB port and the storage device.
Power Up, Expand, and Conquer: Conquering New Frontiers with Expansion Slots and Peripheral Connections
PCIe (Peripheral Component Interconnect Express) slots connect graphics cards, sound cards, and other high-bandwidth peripherals. Understanding PCIe versions and lane configurations is crucial when selecting expansion cards.
You want to install a powerful graphics card to enjoy the latest gaming titles. You’ll need the newest version of PCIe PCIe 5.0, which offers twice the bandwidth of PCIe 4.0. You can enhance your computer’s performance and functionality by connecting faster graphics cards, storage devices, and other peripherals directly to your motherboard.
While PCIe dominates the modern landscape, it’s still important to be familiar with older expansion slots like PCI and AGP (Accelerated Graphics Port). These slots may still be relevant for specific legacy hardware or compatibility needs.
Suppose you have an old sound card or network card that uses a PCI interface. You can find a motherboard with legacy PCI slots to accommodate these older expansion cards, ensuring compatibility with your existing hardware.
However, if you’re building a new PC, you’ll unlikely need to use legacy expansion slots. Most modern motherboards only have PCIe slots.
Motherboards offer an array of I/O ports and connectors for various devices. USB, Ethernet, audio jacks, and video outputs are just a few examples. Understanding the types and quantities of these ports will help you plan your PC’s connectivity options.
Consider your connectivity requirements. If you have multiple USB devices such as a keyboard, mouse, external storage, and peripherals, ensure that the motherboard provides an adequate number of USB ports. Similarly, to connect your PC to a high-resolution monitor, ensure the motherboard has the necessary video outputs, such as HDMI or DisplayPort.
If you don’t have any “old” USB devices, go for a modern motherboard. Modern motherboards typically have Thunderbolt ports, which offer high-speed data transfer speeds. They can connect external storage devices, displays, and other peripherals.
The Role of RAM: Speeding Up Your System
Random Access Memory (RAM) determines your system’s responsiveness. Your computer stores data in its short-term memory while it processes it.
The more RAM you have, the more data your system can store and process. Sufficient RAM can significantly boost performance, particularly for tasks requiring high demands, such as gaming or video editing.
Due to your system’s increased storage and processing capabilities, more RAM can improve performance, particularly for demanding tasks such as gaming and video editing.
Motherboards feature different configurations of RAM slots, such as single-channel, dual-channel, and quad-channel. Understanding these configurations will help you maximize your memory’s performance potential.
For example, if you have a dual-channel memory configuration, you’ll need to install memory modules in pairs, populating two slots of the same color on your motherboard. This configuration provides better memory bandwidth and improves overall system performance.
Power Phases: Keeping Your Components Happy
Power phases on a motherboard regulate and distribute electrical power to various components. More power phases generally result in better stability, improved overclocking potential, and longer component lifespan.
If you’re an enthusiast who wants to push the limits of your hardware through overclocking, a motherboard with more power phases will provide better power delivery and stability, allowing you to achieve higher clock speeds while keeping your components safe.
Now let’s explore the primary power connectors, such as the 24-pin ATX and 4/8-pin CPU power connectors. Understanding these connectors ensures proper power delivery to your motherboard and other components.
When connecting the 24-pin ATX power connector, ensure it firmly clicks into place on the motherboard. Similarly, the 4/8-pin CPU power connector must be securely attached to provide sufficient power to the processor. Failure to properly connect these power connectors can result in system instability or failure to boot.
Journey to the Firmware Realm: BIOS vs. UEFI – The Battle for Superiority
The Basic Input/Output System (BIOS) and Unified Extensible Firmware Interface (UEFI) are firmware interfaces that initialize your motherboard and enable you to configure various settings. Let’s compare the two and lighten the transition from BIOS to UEFI.
BIOS is the older firmware interface, while UEFI is the more modern one. UEFI offers several advantages over BIOS, including a graphical user interface (GUI), support for larger hard drives, and faster boot times. Upgrading the motherboard firmware may pose a risk and should only be done if necessary, as it may require transitioning from BIOS to UEFI.
Now let’s explore essential settings within BIOS/UEFI, such as boot order, overclocking options, and hardware monitoring. Familiarizing yourself with these settings will empower you to optimize your PC’s performance.
Some of the most essential BIOS/UEFI settings include:
- Boot order: This setting determines which storage device your PC boots from.
- Overclocking options: These settings allow you to increase your CPU’s and memory’s clock speed.
- Hardware monitoring: This setting will enable you to monitor the temperature and voltage of your PC’s components.
Troubleshooting Adventures: Unmasking Mysteries and Resurrecting Your Motherboard’s Glory
Let’s discuss common motherboard problems, such as failure to power on, RAM compatibility issues, and BIOS-related concerns. Understanding these issues will help you troubleshoot and resolve them efficiently.
We’ll discuss common motherboard problems, such as failure to power on, RAM compatibility issues, and BIOS-related concerns. Understanding these issues will help you troubleshoot and resolve them efficiently.
Some of the most common motherboard problems include:
- Failure to power on: A faulty power supply unit (PSU), a loose power connection, or a defective motherboard can cause this.
- RAM compatibility issues can occur when you try to install RAM incompatible with your motherboard.
- BIOS-related concerns can occur when your BIOS is corrupted or outdated.8.2 Troubleshooting Steps
Now we can outline a systematic approach to diagnose and resolve motherboard-related issues. You’ll have the tools to confront problems directly, from conducting basic hardware checks to implementing advanced troubleshooting techniques.
The following are some general troubleshooting steps that you can follow if you are experiencing problems with your motherboard:
- Check the power supply unit (PSU). Turn on the PSU and connect the power cables correctly to the motherboard and other components.
- Ensure that you correctly insert the RAM into the motherboard. To fix the problem, try taking out the RAM and putting it back in. It’s essential to install the RAM properly for the best performance.
- Update the BIOS. If your BIOS is outdated, it can cause compatibility issues with your hardware. You can update the BIOS by downloading the latest BIOS update from the motherboard manufacturer’s website.
If you have followed these troubleshooting steps and are still experiencing problems with your motherboard, you may need to contact the manufacturer for further assistance.
Final Thoughts
Congratulations, dear readers, on completing this exciting post on our motherboard exploration. You have delved into your PC’s heart and soul, unraveling the motherboard’s hidden powers. But this is just the beginning of your adventure. There’s still so much more to discover!
Each post will bring you closer to becoming a true master of your PC, enabling you to unleash its full potential and elevate your computing experience to new heights.
Return to my blog site to continue your adventure and unlock the secrets that lie ahead. Unravel the mysteries of memory magic and harness your system’s full speed and responsiveness. Empower your PC with stability and performance, and navigate the firmware realm to optimize your settings.
And when challenges arise, fear not! Our troubleshooting adventures await, ready to equip you with the skills to unmask and resolve common motherboard issues. We’ll guide you step by step, ensuring your PC triumphs over any obstacle that comes its way.
So, dear readers, buckle up and prepare for our exploration’s next chapter. Return to my blog site, where the magic of computers unfolds before your eyes. Unleash your PC’s true potential and become a master of the digital universe. The adventure awaits, and we’ll guide you every step of the way. Your destiny as a PC enthusiast awaits!
Don’t hesitate to contact me with questions or any additional advice/tips about this subject. If you want to keep me in the loop if I upload a new post, subscribe so you receive a notification by e-mail.